
Systemic Breakthroughs in the Copper Tube Industry: How Multi-Factor Collaboration is Redefining the Boundaries of Industrial Competitiveness
Subtitle: As the dividends of single technological innovations diminish, the quadruple synergy of technology, management, policy, and markets is becoming the new engine for industry value leapfrogging—how does this systemic capability, possessed by only 20% of leading enterprises, contribute to 50% of the industry's profit growth?
Technology-Management Synergy: How Smart Manufacturing Reconstructs the Production Function
Traditional copper tube enterprise competition often focused on equipment upgrades or process optimization, whereas systemic breakthroughs demand the deep integration of technology and management. The digital transformation of Hailiang Co., Ltd. serves as a prime example. Its self-developed fifth-generation low-carbon intelligent coil production line increased copper billet extension speed from 1.5 meters per minute to 2.4 meters and optimized six melting furnaces down to one shaft furnace, boosting production efficiency by 60% and reducing carbon emissions by 30%. However, the truly disruptive benefits came from the simultaneous restructuring of management models—integrating SAP, OA, and MES systems to create a "digital cockpit" enabled full-process data transparency, slashing order response time from 3-5 days to 4-6 hours and reducing inventory turnover days from 48 to 33.
Table: Comparison of key indicators of intelligent manufacturing upgrade
|
Performance indicators |
Traditional production mode |
After digital transformation |
Improved performance |
|
R&D cycle |
2-3 years |
6-12 months |
60% reduction |
|
Achievement conversion rate |
Approx. 15% |
More than 40% |
Nearly 2 times |
|
Product premium ability |
benchmark |
6x improvement |
Significantly enhanced |
|
Market share increased |
Slow growth |
Global segment accounts for 60% |
Leapfrog development |
This synergistic effect is particularly evident in quality control. Guangdong Longfeng Precision Copper Tube introduced an AI visual inspection system trained on 100,000 defect samples, lowering the defect rate to 0.3‰. Yet, the efficiency gains from inspection relied on organizational change—the traditional quality inspection department was restructured into a "data decision-making group," reducing quality inspectors by 80% while increasing the proportion of data analysts from 5% to 30%. A more profound impact is the shift in production logic: Jiangsu Cuilong's cleaning-free process, achieved through innovative cracking-type lubricant formulations, eliminated the cleaning step. However, realizing its full value required matching production line restructuring, shortening the cycle time from stretching to annealing from 48 hours to 24 hours. This "twin-drive" of technology and management enables leading enterprises to achieve an annual output per capita of 350 tons, three times the industry average.
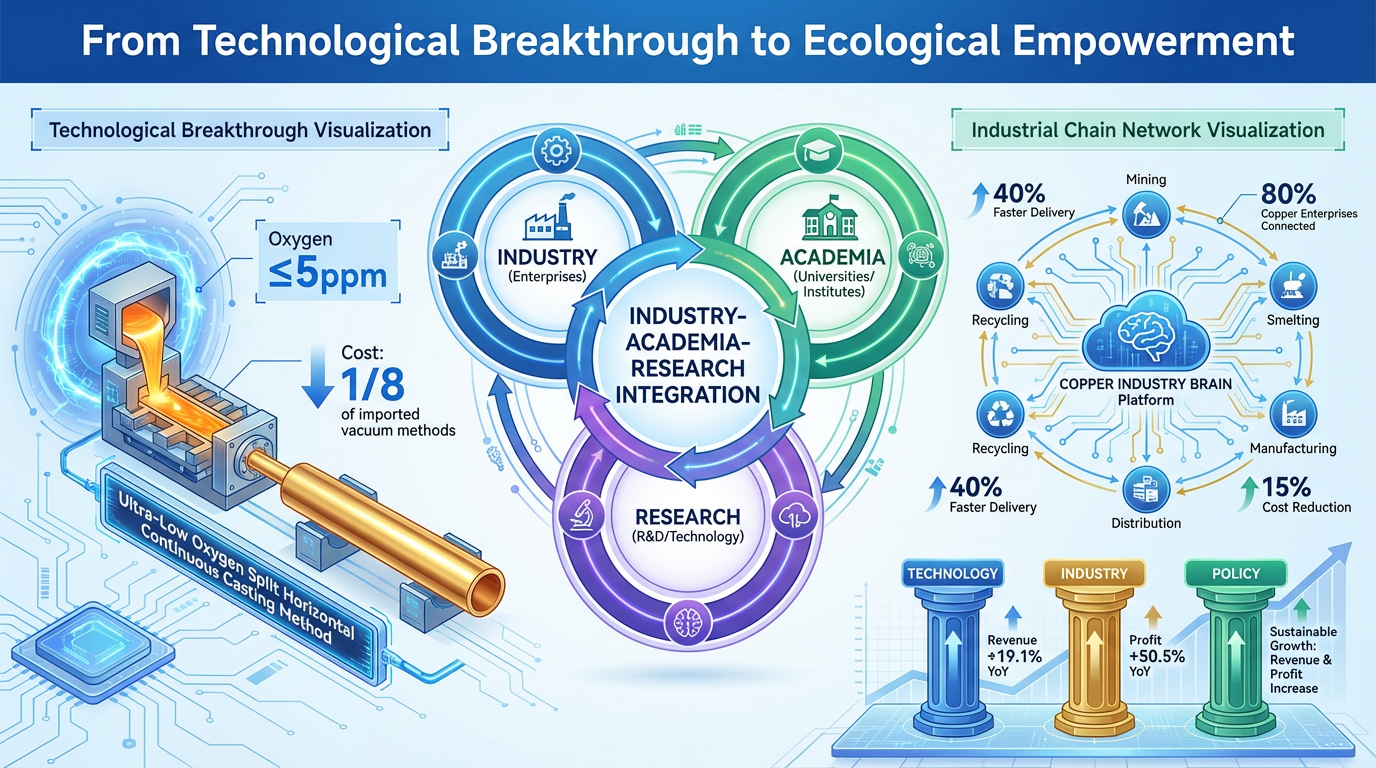
Industry-Academia-Research & Industrial Chain Synergy: The Leap from "Technological Breakthrough" to "Ecological Empowerment"
The innovation model in the copper tube industry is shifting from "single-point R&D" to "system integration." The successful collaboration between Jiangxi Naile Copper Co., Ltd. and Nanchang University demonstrates that deep industry-academia-research integration requires establishing three mechanisms: demand matching, resource integration, and benefit sharing. To tackle the industry challenge of achieving oxygen content ≤5ppm in copper tubes for semiconductors, the university-enterprise joint team developed an "ultra-low oxygen split horizontal continuous casting method," reducing costs to one-eighth of imported vacuum methods. However, releasing the value of this technological breakthrough required industrial chain synergy—Naile Copper used it to enter the global chip supply chain, increasing processing fees sixfold.
The scope of collaboration is expanding to the entire chain. Jiangxi copper enterprises built a "Copper Industry Brain" that connects 80% of the city's copper enterprises, enabling capacity sharing and order coordination through big data analysis. This platform approach allows SMEs to participate in high-end competition: when one company receives a super-large order, the system automatically splits it among multiple factories for parallel production, reducing delivery time by 40% and costs by 15%. On the policy front, the "Copper Industry High-Quality Development Implementation Plan (2025-2027)" explicitly supports building innovation consortia, aiming to overcome 10-12 "bottleneck" technologies within three years. This three-dimensional "technology-industry-policy" synergy contributed to Jiangxi's copper industry achieving a 19.1% year-on-year revenue growth and a 50.5% profit increase in the first three quarters of 2025.
(This image was generated by AI.)
Green-Digital Synergy: Dual Benefits of Sustainable Development and Cost Efficiency
The green transition in the copper tube industry is generating a "multiplier effect" with digitalization. Hailiang Co., Ltd.'s zero-carbon factory, utilizing photovoltaic power and carbon capture technology, reduced the product carbon footprint by 53%. However, activating the value of carbon reduction data requires digital tools—its carbon footprint tracking system monitors electricity consumption in real-time across all processes, reducing comprehensive energy consumption per unit product by 30%. This synergy helps products qualify for EU CBAM tax exemptions, increasing premiums by 15%.
Similar synergistic value is evident in the circular economy. Jiangxi Baotai Group established a closed-loop recycling system achieving a 95% reuse rate for waste copper tubes. However, maximizing economic benefits relies on IoT technology—using RFID chips to trace the source of each ton of scrap copper ensures recycled copper purity reaches 99.99%, costing 30% less than primary copper. A more cutting-edge innovation is carbon-solidifying copper tubes, which add carbonate minerals to the tube wall coating to solidify 50 kg of CO₂ per ton of product. However, commercialization requires a carbon asset management system to convert emission reductions into carbon quotas for trading. The deep integration of green and digital technologies allows leading enterprises not only to avoid environmental risks but also to tap into a green premium market growing at 25% annually.
Domestic-International Synergy: Optimal Resource Allocation Under Dual Circulation
Amid geopolitical shifts, leading enterprises are enhancing resilience through coordinated domestic and international layouts. The case of Jinlong Copper Tube Group is typical: its US factory leverages USMCA rules of origin for tariff-free access to the North American market. Simultaneously, its domestic base focuses on R&D for ultra-thin wall copper tubes (wall thickness ≤0.25mm), using gradient wall thickness technology to reduce costs by 20%. This "R&D in China + Manufacturing Overseas" model helped the company maintain a 15% market share during US tariff disputes.
Collaboration strategies are evolving into multi-level approaches. Hailiang Co., Ltd. established production bases in Indonesia and Morocco to adapt to regional needs. Jiangxi copper enterprises adopt an "overseas base + local R&D" model, collaborating with local research institutions to develop corrosion-resistant copper tubes suited to local climates. Policy-wise, the Implementation Plan explicitly supports enterprises in participating in international standard setting, promoting the "going global" of Chinese technology. This synergy of domestic and international capabilities enabled China's copper tube exports to grow by 14% in 2025, with the share of high-end products increasing from 15% to 35%.
Organization-Talent Synergy: Institutionalizing the Innovation Gene
Systemic breakthroughs ultimately depend on organization and talent synergy. The "Chief Technology Officer (CTO) mechanism" adopted by Jiangxi Naile Copper and Nanchang University embeds university experts directly into production lines, solving the "disconnect" between research and production. However, sustained innovation requires institutional design—enterprises allocate 8%-12% of sales revenue to R&D, with 30% directed to support CTO projects, creating a "R&D-profit-reinvestment" closed loop.
Talent cultivation models are being revolutionized simultaneously. Jiangxi University of Science and Technology's "Outstanding Engineer Plan" implements segmented training: graduate students focus on coursework in their first year and participate in actual enterprise projects from the second year onwards. Enterprises, in turn, engage through the "Industry Professor" system, where technical backbone personnel participate in teaching. This synergy results in over 90% of graduates finding jobs matching their specialties, and enterprise R&D teams gain continuous innovation capability. At the organizational level, Hailiang Co., Ltd. established "Joint Innovation Laboratories", collaborating with Huawei to develop vertical large models for the non-ferrous metals industry, increasing process parameter optimization efficiency by 40%. This triangular synergy of "institution-talent-organization" forms the underlying support for iterative enterprise innovation.
Synergistic Effects Become the New Competitive Barrier
Competition in the copper tube industry is shifting from "factor-driven" to "system-driven collaboration." Enterprises that achieve the five-fold synergy of technology & management, industry-academia-research & industrial chain, green & digital, domestic & international, and organization & talent, not only enjoy over 30% comprehensive efficiency gains but also build replicable competitive barriers. As demonstrated by the Jiangxi copper industry case: systemic collaboration enabled regional enterprises to improve product yield by 5 percentage points, shorten R&D cycles by 60%, and gain sustained premium pricing power in the global market.
Over the next five years, industry polarization will accelerate. The mere 20% of enterprises possessing systemic capabilities are likely to contribute 50% of the industry's profit growth. For enterprises, the focus must shift from pursuing "single-point advantages" to building "collaborative networks," using mechanism design to stimulate chemical reactions across elements. As one industry expert stated: "The future champion enterprises will not be leaders in a specific technology or product, but the 'system engineers' most adept at integrating multidimensional resources".
Productos relacionados
-

El tubo de cobre está hecho de material de cobre de alta pureza con un contenido de cobre de no menos del 99.9%. Los códigos del material principal so...
Ver detalles -

Los tubos de cobre de paredes gruesas también se llaman tubos de cobre de paredes gruesas sin costura. Los tubos de cobre de paredes gruesas se fabric...
Ver detalles -
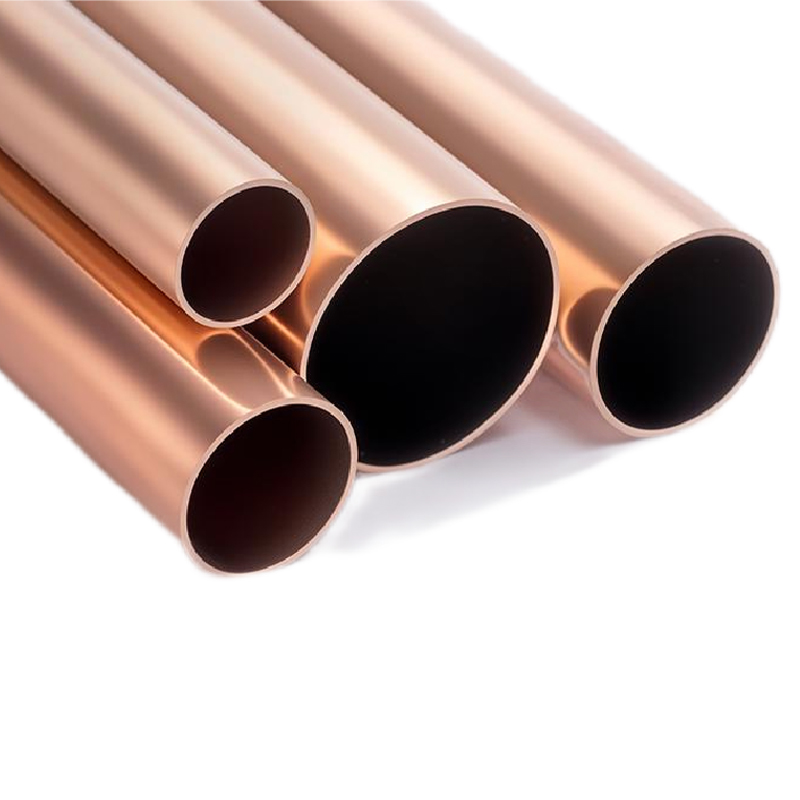

El tubo de agua de cobre producido por nuestra empresa es un tubo de cobre de alto rendimiento adecuado para sistemas de agua fría y caliente y aplica...
Ver detalles -
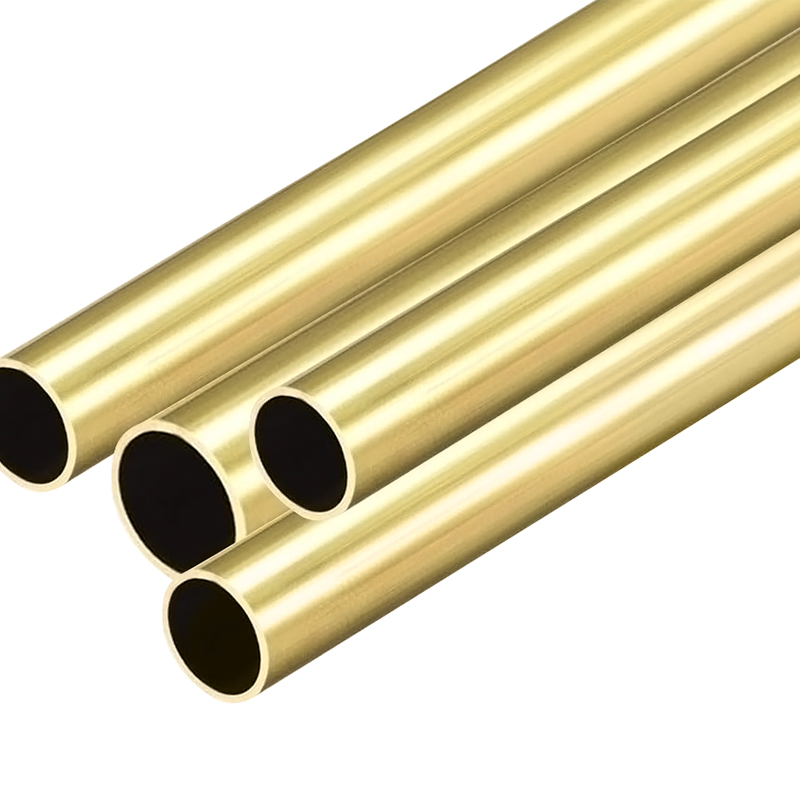

El latón es una aleación de cobre y zinc. Tiene un buen procesamiento y propiedades mecánicas, por lo que se usa ampliamente en la fabricación de tubo...
Ver detalles -
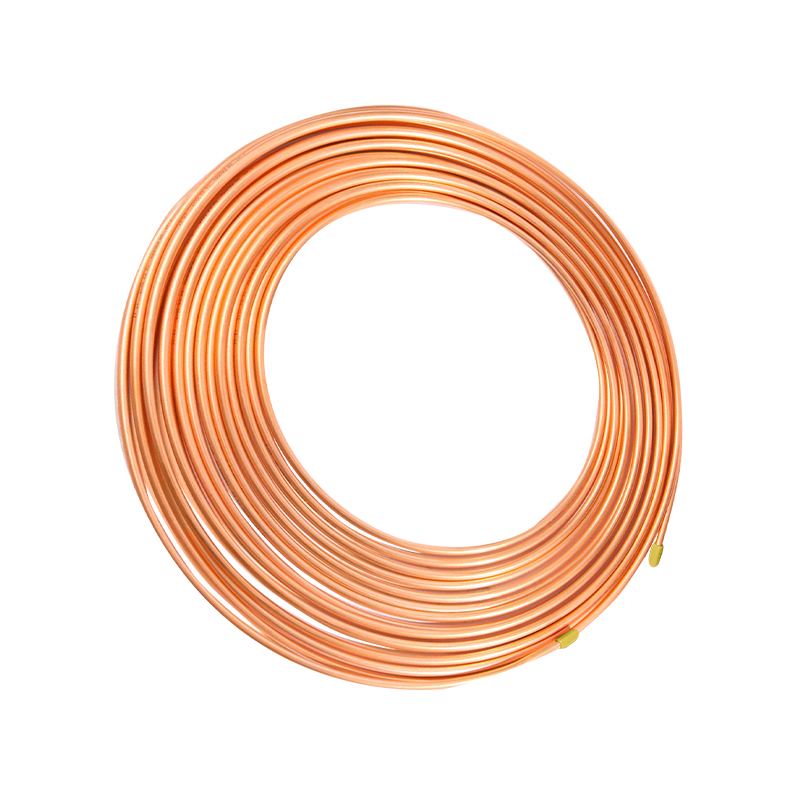

El tubo capilar de cobre generalmente se fabrica mediante mecanizado de precisión, y su precisión dimensional puede alcanzar una milésima de pulgada. ...
Ver detalles -
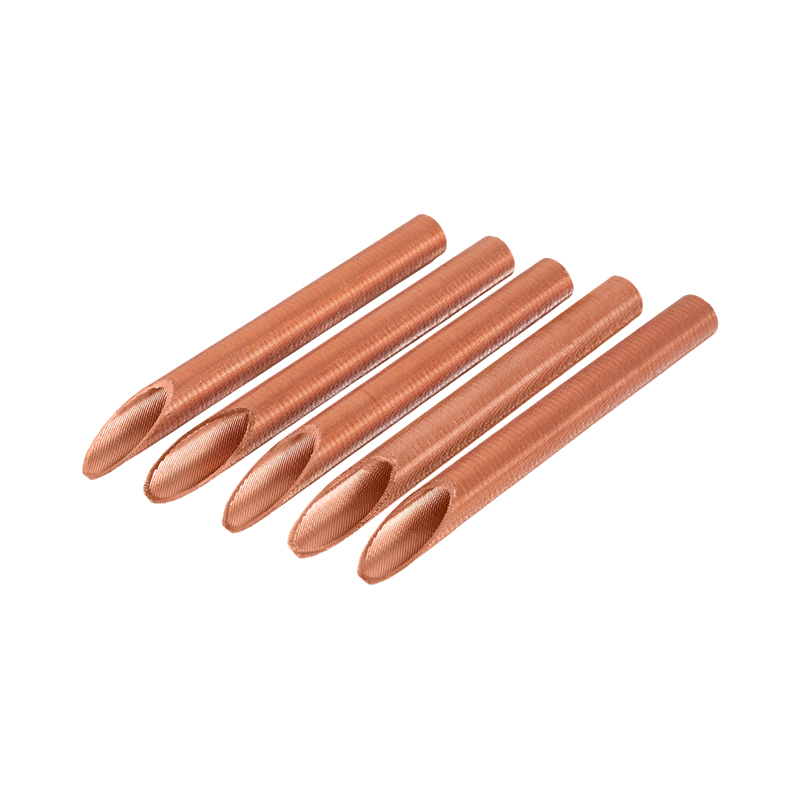

El tubo de cobre del condensador adopta un diseño patentado desarrollado independientemente por la compañía, y los extremos de las aletas están provis...
Ver detalles -

El tubo del evaporador de cobre adopta un diseño de aleta único, y las aletas externas están equipadas con canales interconectados especialmente diseñ...
Ver detalles -

El tubo de cobre de aleta es un elemento de intercambio de calor altamente eficiente. Su característica estructural es que se forman aletas uniformes ...
Ver detalles

 English
English Español
Español